




Common Desktop Environment: ToolTalk Messaging Overview
Contents of Chapter:
- What Kind of Work Problems Can the ToolTalk Service Solve?
-
- Tool Inter-changeability
-
- Control Integration
-
- Network-Transparent Events
-
- Automatic Tool Invocation
-
- Distributed-Object System
-
- Persistent Objects
-
- Scenarios Illustrating How the ToolTalk Service Helps Solve Work Problems
-
- How Applications Use ToolTalk Messages
-
- Sending ToolTalk Messages
-
- Message Patterns
-
- Receiving ToolTalk Messages
-
- ToolTalk Message Distribution
-
- Process-Oriented Messages
-
- Object-Oriented Messages
-
- Determining Message Delivery
-
- Modifying Applications to Use the ToolTalk Service
-
As computer users increasingly demand that independently developed applications work together, inter-operability is becoming an important theme for software developers. By cooperatively using each other's facilities, inter-operating applications offer users capabilities that would be difficult to provide in a single application. The ToolTalk service is designed to facilitate the development of inter-operating applications that serve individuals and work groups.
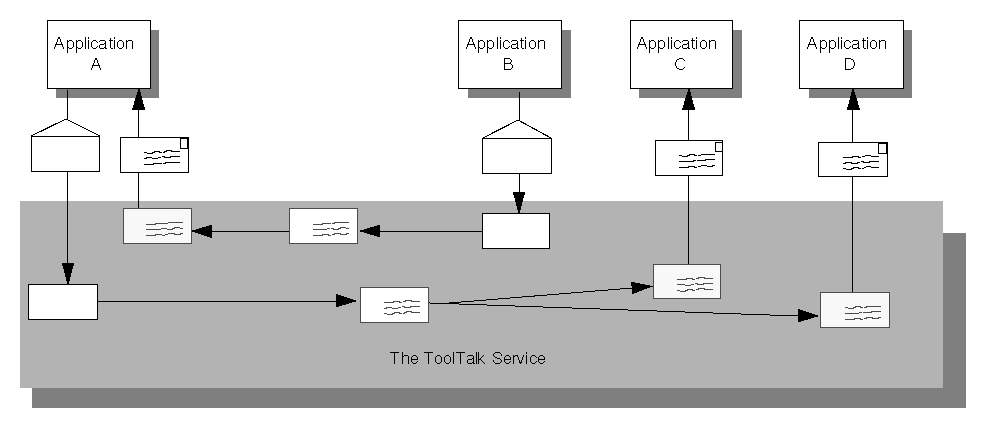
The ToolTalk service enables independent applications to communicate with each other without having direct knowledge of each other. Applications create and send ToolTalk messages to communicate with each other. The ToolTalk service receives these messages, determines the recipients, and then delivers the messages to the appropriate applications, as shown in Figure 1-1.
Figure 1-1 Applications Using the ToolTalk Service
What Kind of Work Problems Can the ToolTalk Service Solve?
This section describes some of the inter-operability problems the ToolTalk service is designed to solve. The ToolTalk service is the appropriate technology to use if your application needs:
- Tool inter-changeability
- Control integration
- Network-transparent events that are not owned by any well-known server (for example, an X server) and that do not have any predictable set of listeners
- Automatic tool invocation
- A widely-available distributed object system
- Persistent objects
Of course, there are some inter-operability problems for which the ToolTalk service may not be the appropriate technology to use. However, when your application needs to solve both sorts of problems (that is, a combination of those inter-operability problems for which the ToolTalk service is designed to solve and those problems for which it is not designed), you can use the ToolTalk service in combination with other technologies.
Tool Inter-changeability
Use the ToolTalk service when you want plug-and-play capability. The term plug-and-play means that any tool can be replaced by any other tool that follows the same protocol. That is, any tool that follows a given ToolTalk protocol can be placed (plugged) into your computing environment and perform (play) those functions indicated by the protocol. Tools can be mixed and matched, without modification and without having any specific built-in knowledge of each other.
Control Integration
Use the ToolTalk service when your application requires control integration. The term control integration indicates a group of tools working together toward a common end without direct user intervention. The ToolTalk service enables control integration through its easy and flexible facilities for issuing arbitrary requests, either to specific tool instances or to anonymous service providers.
Network-Transparent Events
Use the ToolTalk service when your application needs to generate or receive network-transparent events. To be useful, traditional event mechanisms (such as signals and window-system events) require special circumstances; for example, you must know a process or window ID. The ToolTalk service allows events to be expressed naturally: in terms of the file to which the event refers, or the group of processes on the network to which the event is applicable. The ToolTalk service delivers events (called notices) to any interested process anywhere on the network. ToolTalk notices are a flexible and easy way to provide extensibility for your system.
Automatic Tool Invocation
Use the ToolTalk service when your application needs network-transparent automatic invocation. The ToolTalk service lets you describe the messages that, when sent from any location on the network, should cause your tool to be invoked. The ToolTalk auto-start facility is easier to use and less host-specific than the conventional inetd(1) facility.
Distributed-Object System
Use ToolTalk when you need to build your application on a distributed-object system that is available across a wide variety of platforms. ToolTalk's object system can be used by any application on all the popular UNIX platforms, regardless of whether the application
- Is single- or multi-threaded
- Has a command-line or graphical user interface
- Uses its own event loop, or that of a window-system toolkit
Note: Programs coded to the ToolTalk object-oriented messaging interface are not portable to CORBA-compliant systems without source changes.
Persistent Objects
Use the ToolTalk service when your application needs to place objects unobtrusively in the UNIX file system.
Scenarios Illustrating How the ToolTalk Service Helps Solve Work Problems
The scenarios in this section illustrate how the ToolTalk service helps users solve their work problems. The message protocols used in these scenarios are hypothetical.
Using the ToolTalk Desktop Services Message Set
The ToolTalk Desktop Services Message Set allows an application to integrate and control other applications without user intervention. This section presents two scenarios ("The Smart Desktop" and "Integrated Toolsets") that show how the Desktop Services Message Set might be implemented.
Note: The scenario in this section is intended to illustrate how the ToolTalk service can be used in an application-level program that interprets user requests; it is not intended to illustrate how the Common Desktop Environment product implements the ToolTalk service to interpret user requests.
A common user requirement for a graphic user interface (GUI) front-end is the ability to have data files be aware (or "know") of their applications. To do this, an application-level program is needed to interpret the user's requests. Examples of application-level programs (known as smart desktops) are the Apple Macintosh(R) finder, Microsoft WindowsTM File Manager, and the Common Desktop Desktop File Manager. The key common requirements for smart desktops are:
- Takes a file
- Determines its application
- Invokes the application
The ToolTalk Service provides additional flexibility by allowing classes of tools to edit a specific data type. The following scenario illustrates how the Desktop Services Message Set might be implemented as a smart desktop transparent to the end-user.
- Diane double-clicks on the File Manager icon.
- The File Manager opens and displays the files in Diane's current directory.
- Diane double-clicks on an icon for a data file.
a. The File Manager requests that the file represented by the icon be displayed. The File Manager encodes the file type in the display message.
b. The ToolTalk session manager matches the pattern in the display message to a registered application (in this case, the Icon Editor), and finds an instance of the application running on Diane's desktop.
Note: If the ToolTalk session manager does not find a running instance of the application, it checks the statically-defined process types (ptypes) and starts an application that best matches the pattern in the message. If none of the ptypes matches, the session manager returns failure to the File Manager application.
c. The Icon Editor accepts the display message, de-iconifies itself, and raises itself to the top of the display.
- Diane manually edits the file.
Another significant application for which the Desktop Services Message Set can be implemented is integrated toolsets. These environments can be applied in vertical applications (such as a CASE developer toolset) or in horizontal environments (such as compound documents). Common to both of these applications is the premise that the overall solution is built from specialized applications designed to perform one particular task well. Examples of integrated toolset applications are text editors, drawing packages, video or audio display tools, compiler front-ends, and debuggers. The integrated toolset environment requires applications to interact by calling on each other to handle user requests. For example, to display video, an editor calls a video display program; or to check a block of completed code, an editor calls a compiler.
The following scenario shows how the Desktop Services Message Set might be implemented as an integrated toolset:
- Bruce is working on a compound document using his favorite editor.
He decides to change the some of the source code text.
- Bruce double-clicks on the source code text.
a. The Document Editor first determines the text represents source code and then determines which file contains the source code.
b. The Document Editor sends an edit message request, using the file name as a parameter for the message.
c. The ToolTalk session manager matches the pattern in the edit message to a registered application (in this case, the Source Code Editor), and finds an instance of the application running on Bruce's desktop.
Note: If the ToolTalk session manager does not find a running instance of the application, it checks the statically-defined ptypes and starts an application that best matches the pattern in the message. If none of the ptypes matches, the session manager returns failure to the Document Editor application.
d. The Source Code Editor accepts the edit message request.
e. The Source Code Editor determines that the source code file is under configuration control, and sends a message to check out the file.
f. The Source Code Control application accepts the message and creates a read-write copy of the requested file. It then passes the name of the file back to the Source Code Editor.
g. The Source Code Editor opens a window that contains the source file.
- Bruce edits the source code text.
Using the ToolTalk Document and Media Exchange Message Set
The ToolTalk Document and Media Exchange Message Set is very flexible and robust. This section illustrates three uses of the ToolTalk Document and Media Exchange Message Set:
- Integrating multimedia into an authoring application
- Adding multimedia extensions to an existing application
- Extending the cut-and-paste facility of X with a media-translation facility
Integrating Multimedia Functionality
Integrating multimedia functionality into an application allows end-users of the application to embed various media types in their documents.
Typically, an icon that represents the media object is embedded in the document. Upon selection of an embedded object, the ToolTalk service automatically invokes an appropriate external media application and the object is played as illustrated in the following scenario.
- Daniel opens a document that contains multimedia objects.
- The window shows the document with several icons representing various media types (such as sound, video, and graphics).
- Daniel double-clicks on the sound icon.
A sound application (called a player) is launched and the embedded recording is played.
- To edit the recording, Daniel clicks once on the icon to select it and uses the third mouse button to display an Edit menu.
An editing application is launched, and Daniel edits the media object.
Adding Multimedia Extensions to Existing Applications
The ToolTalk Document and Media Exchange Message Set also allows an application to use other multimedia applications to extend its features or capabilities. For example, a Calendar Manager can be extended to use the Audio Tool to play a sound file as a reminder of an appointment, as illustrated in the following scenario:
- Shelby opens her Calendar Manager and sets an appointment.
- Shelby clicks on an Audio Response button, which causes the Audio Tool to start.
- Shelby records her message; for example, "Bring the report."
When Shelby's appointment reminder is executed, the Calendar Manager will start the Audio Tool and play Shelby's recorded reminder.
Extending the X Cut-and-Paste Facility
The ToolTalk Document and Media Exchange Message Set can support an extensible, open-ended translation facility. The following scenario illustrates how an extensible multimedia cut and paste facility could work:
- Maria opens two documents that are different media types.
- Maria selects a portion of Document A and cuts the portion using the standard X-windowing cut facility.
- Maria then pastes the cut portion into Document B.
a. Document B negotiates the transfer of the cut data with Document A.
b. If Document B does not understand any of the types offered by Document A, it requests that Document A sends it a tagged media type. Document B uses the tagged media type to broadcast a ToolTalk message requesting a translation of the media type to a media type it understands.
c. A registered translation utility accepts the request and returns the translated version of the media type to Document B.
d. The paste of the translated data into Document B is performed.
Applications create, send, and receive ToolTalk messages to communicate with other applications. Senders create, fill in, and send a message; the ToolTalk service determines the recipients and delivers the message to the recipients. Recipients retrieve messages, examine the information in the message, and then either discard the message or perform an operation and reply with the results.
ToolTalk messages are simple structures that contain fields for address, subject, and delivery information. To send a ToolTalk message, an application obtains an empty message, fills in the message attributes, and sends the message. The sending application needs to provide the following information:
- Is the message a notice or a request (that is, should the recipient respond to the message)?
- What interest does the recipient share with the sender? (For example, is the recipient running in a specific user session or interested in a specific file?)
To narrow the focus of the message delivery, the sending application can provide more information in the message.
Message Patterns
An important ToolTalk feature is that senders need to know little about the recipients because applications that want to receive messages explicitly state what message they want to receive. This information is registered with the ToolTalk service in the form of message patterns.
Applications can provide message patterns to the ToolTalk service at installation time and while the application is running. Message patterns are created similarly to the way a message is created; both use the same type of information. For each type of message an application wants to receive, it obtains an empty message pattern, fills in the attributes, and registers the pattern with the ToolTalk service. These message patterns usually match the message protocols that applications have agreed to use. Applications can add more patterns for individual use.
When the ToolTalk service receives a message from a sending application, it compares the information in the message to the register patterns. Once matches have been found, the ToolTalk service delivers copies of the message to all recipients.
For each pattern that describes a message an application wants to receive, the application declares whether it can handle or observe the message. Although many applications can observe a message, only one application can handle the message to ensure that a requested operation is performed only once. If the ToolTalk service cannot find a handler for a request, it returns the message to the sending application indicating that delivery failed.
When the ToolTalk service determines that a message needs to be delivered to a specific process, it creates a copy of the message and notifies the process that a message is waiting. If a receiving application is not running, the ToolTalk service looks for instructions (provided by the application at installation time) on how to start the application.
The process retrieves the message and examines its contents.
- If the message contains a notice that an operation has been performed, the process reads the information and then discards the message.
- If the message contains a request to perform an operation, the process performs the operation and returns the result of the operation in a reply to the original message. Once the reply has been sent, the process discards the original message.
ToolTalk Message Distribution
The ToolTalk service provides two methods of addressing messages: process-oriented messages and object-oriented messages.
Process-Oriented Messages
Process-oriented messages are addressed to processes. Applications that create a process-oriented message address the message to either a specific process or to a particular type of process. Process-oriented messages are a good way for existing applications to begin communication with other applications. Modifications to support process-oriented messages are straightforward and usually take a short time to implement.
Object-Oriented Messages
Object-oriented messages are addressed to objects managed by applications. Applications that create an object-oriented message address the message to either a specific object or to a particular type of object. Object-oriented messages are particularly useful for applications that currently use objects or that are to be designed around objects. If an existing application is not object-oriented, the ToolTalk service allows applications to identify portions of application data as objects so that applications can begin to communicate about these objects.
Note: Programs coded to the ToolTalk object-oriented messaging interface are not portable to CORBA-compliant systems without source changes.
Determining Message Delivery
To determine which groups receive messages, you scope your messages. Scoping limits the delivery of messages to a particular session or file.
Sessions
A session is a group of processes that have an instance of the ToolTalk message server in common. When a process opens communication with the ToolTalk service, a default session is located (or created, if a session does not already exist) and a process identifier (procid) is assigned to the process. Default sessions are located either through an environment variable (called "process tree sessions") or through the X display (called "X sessions").
The concept of a session is important in the delivery of messages. Senders can scope a message to a session and the ToolTalk service will deliver it to all processes that have message patterns that reference the current session. To update message patterns with the current session identifier (sessid), applications join the session.
Files
A container for data that is of interest to applications is called a file in this book.
The concept of a file is important in the delivery of messages. Senders can scope a message to a file and the ToolTalk service will deliver it to all processes that have message patterns that reference the file without regard to the process's default session. To update message patterns with the current file path name, applications join the file.
You can also scope a message to a file within a session. The ToolTalk service will deliver the message to all processes that reference both the file and session in their message patterns.
Note: The file scoping feature is restricted to NFS and UFS file systems.
and UFS file systems.
Before you modify your application to use the ToolTalk service, you must define (or locate) a ToolTalk message protocol: a set of ToolTalk messages that describe operations applications agree to perform. The message protocol specification includes the set of messages and how applications should behave when they receive the messages.
To use the ToolTalk service, an application calls ToolTalk functions from the ToolTalk API. The ToolTalk API provides functions to register with the ToolTalk service, to create message patterns, to send messages, to receive messages, to examine message information, and so on. To modify your application to use the ToolTalk service, you must first include the ToolTalk API header file in your program. You also need to modify your application to:
- Initialize the ToolTalk service and join a session
- Register message patterns with the ToolTalk service
- Send and receive messages
- Unregister message patterns and leave your ToolTalk session





Generated with CERN WebMaker











