





#include <Tt/tt_c.h>
tt_error
void tt_error(const char *funcname, Tt_status status)
The tt_error function is a publicly-known null function. This function is called by the ToolTalk library just before it returns from any ToolTalk API call that has a status other than TT_OK. The name of the function that is about to return and the status code is passed. You can use this call to set a dbx breakpoint in tt_error to quickly catch and trace back any ToolTalk errors. You can also interpose this function, for example, to log ToolTalk errors to stderr. The following code example shows how an application might do this.
void tt_error(const char *funcname, Tt_status status) {
fprintf(stderr, "ToolTalk function %s returned %s.\n",
funcname, tt_status_message(status));
}
tt_file_netfile
char * tt_file_netfile( const char * filename );
The tt_file_netfile function maps between local and canonical path names. It converts the file specified in filename to a netfilename that can be passed to other hosts on the network. The filename is an absolute or relative path name that is valid on the local host. The last component of filename is not required; however, every other component of filename must exist.
This function returns either an error pointer or, if successful, a newly-allocated null-terminated string of an unspecified format, which may be passed to the tt_netfile_file function.
Use tt_ptr_error to extract a status from an error pointer. Possible errors are described in Table C-1.
Table C-1 Possible Errors Returned by tt_file_netfile 
To free allocated strings, use either the tt_free or tt_release call.
To convert the file back to a local file name for the same file, use the tt_netfile_file function.
tt_host_file_netfile
char *tt_host_file_netfile( const char * host,
const char * filename );
The tt_host_file_netfile function maps between local and canonical path names on a remote host. It converts the file specified in host to a netfilename that can be passed to other hosts on the network. The filename is an absolute or relative path name that is valid on the remote host. The last component of filename is not required; however, every other component of filename must exist.
This function returns either an error pointer or, if successful, a newly-allocated null-terminated string of an unspecified format, which may be passed to the tt_netfile_file function.
Use tt_ptr_error to extract a status from an error pointer. Possible errors are described in Table C-2.
Table C-2 Possible Errors Returned by tt_host_file_netfile 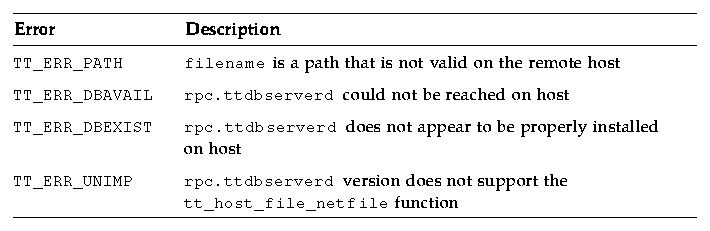
To convert the file back to a local file name for the same file, use the tt_host_netfile_file function.
tt_host_netfile_file
char *tt_host_netfile_file( const char * host,
const char * netfilename );
The tt_host_file_netfile function maps between local and canonical path names on the remote host. It converts the file specified netfilename to a path namethat is valid on the remote host. The netfilename is a copy of a null-terminated string returned by the tt_netfile_file function.
If the specified file is not currently mounted on the local host, a path name in the form of
/DTMOUNTPOINT/host/filepath
is constructed, where:
DTMOUNTPOINT is the intended mount point for the automounter's host map. You can also specify this mount point with the environment variable DTMOUNTPOINT.This function returns either an error pointer or, if successful, a newly-allocated null-terminated local file name.host is the host that contains the file.
filepath is the path to the file contained on the host.
Use tt_ptr_error to extract a status from an error pointer. Possible errors are described in Table C-3.
Table C-3 Possible Errors Returned by tt_host_netfile_file 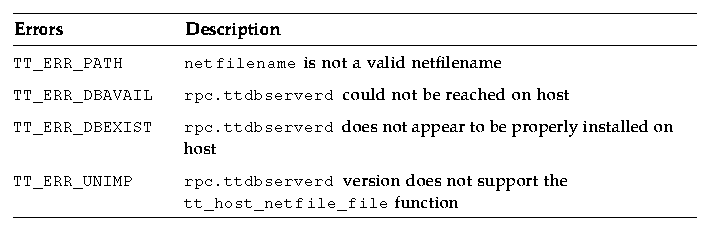
To free allocated strings, use either the tt_free or tt_release call.
To convert the file back to a local file name for the same file, use the tt_host_file_netfile function.
tt_message_print
char * tt_message_print(Tt_message m);
The tt_message_print function allows you to print out messages that are received by not understood. To free allocated strings, use either the tt_free or tt_release call.
This function returns either the error TT_ERR_POINTER or, if successful, the message m in a buffer allocated by ToolTalk (in the same manner as is done in other ToolTalk API calls such as tt_X_session).
tt_netfile_file
char * tt_netfile_file( const char * netfilename );
The tt_netfile_file function maps between canonical and local path names. It converts the file specified netfilename to a path name that is valid on the local host. The netfilename is a copy of a null-terminated string returned by tt_netfile_file.
If the specified file is not currently mounted on the local host, a path name in the form of
/DTMOUNTPOINT/host/filepath
is constructed, where:
DTMOUNTPOINT is the intended mount point for the automounter's host map. You can also specify this mount point with the environment variable DTMOUNTPOINT.This function returns either an error pointer or, if successful, a newly-allocated null-terminated local file name.host is the host that contains the file.
filepath is the path to the file contained on the host.
Use tt_ptr_error to extract a status from an error pointer. Possible errors are described in Table C-4.
Table C-4 Possible Errors Returned by tt_netfile_file 
To free allocated strings, use either the tt_free or tt_release call.
To convert the file back to a net file name for the same file, use the tt_file_netfile function.
tt_pattern_print
char * tt_message_print(Tt_pattern p);
The tt_pattern_print function allows you to print out patterns. To free allocated strings, use either the tt_free or tt_release call.
This function returns either the error TT_ERR_POINTER or, if successful, the pattern p in a buffer allocated by ToolTalk (in the same manner as is done in other ToolTalk API calls such as tt_X_session).




