2 Hardware Requirements and Restrictions
This chapter describes the hardware requirements and
restrictions for a TruCluster Server cluster.
It includes lists of supported cables, trilink connectors, Y cables,
and terminators.
The chapter discusses the following topics:
For the latest information about supported hardware, see the
AlphaServer options list for your system at the following URL:
http://www.compaq.com/alphaserver/products/options.html
2.1 TruCluster Server Member System Requirements
The requirements for member systems in a TruCluster Server cluster
are as follows:
Each supported member system requires a minimum firmware
revision.
See the
Release Notes Overview
supplied with the
AlphaTM
Systems Firmware Update CD-ROM.
You can also obtain firmware information from the Web at the
following URL:
http://www.compaq.com.
Select
software & drivers, in the
support
column, then select
AlphaServer, in the
servers
column.
Select the appropriate system.
Alpha System Reference Manual (SRM) console firmware Version 5.7
or later must be installed on any cluster member that boots from a
disk behind an HSZ80, HSG60, or HSG80 controller.
If the cluster member is
using earlier firmware, the member may fail to boot, indicating
"Reservation Conflict" errors.
TruCluster Server Version 5.1A supports eight-member cluster
configurations as follows:
Fibre Channel: Eight-member systems may be connected to common storage
over Fibre Channel in a fabric (switch) configuration.
Parallel SCSI: Only four of the member systems may be
connected to any one SCSI bus, but you can have multiple SCSI
buses connected to different sets of nodes, and the sets of nodes
may overlap.
We recommend you use a DS-DWZZH-05 UltraSCSI hub
with fair arbitration enabled when connecting four-member systems
to a common SCSI bus using RAID array controllers.
Illustrations of an externally terminated eight-node cluster are
shown in
Chapter 11.
The cluster shown is more
appropriate for high performance technical computing (HPTC)
customers who are looking for performance instead of availability.
The following items pertain to the AlphaServer GS80/160/320
systems:
High power peripheral component interconnect (PCI) modules
(approximately 25 watts or greater) must be placed in PCI slots with a
1-inch module pitch; any slot except 0-5, 0-6, 1-5, and 1-6.
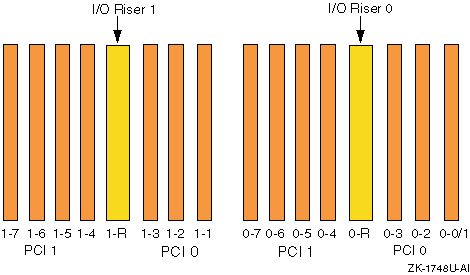
A primary or expansion PCI drawer contains two
3-slot PCI buses and two 4-slot PCI buses (see
Figure 2-1):
PCI0 for I/O riser 0: Slots 0-0/1, 0-2, and 0-3
PCI1 for I/O riser 0: Slots 0-4, 0-5, 0-6, and 0-7
PCI0 for I/O riser 1: Slots 1-1, 1-2, and 1-3
PCI1 for I/O riser 1: Slots 1-4, 1-5, 1-6, and 1-7
Note
Slot 0-0/1 in a primary PCI drawer contains the standard I/O
module.
Figure 2-1: PCI Backplane Slot Layout
TruCluster Server does not support the XMI CIXCD on an AlphaServer
8x00, GS60, GS60E, or GS140 system.
2.2 Memory Channel Restrictions
The Memory Channel interconnect is one method used for cluster
communications between the member systems.
There are currently three versions of the
Memory Channel product: Memory Channel 1, Memory Channel 1.5, and Memory Channel 2.
The
Memory Channel 1 and Memory Channel 1.5 products are very similar (the PCI
adapter for both versions is the CCMAA module) and are generally
referred to as MC1 throughout this manual.
The Memory Channel 2 product
(CCMAB module) is referred to as MC2.
Ensure that you abide by the following Memory Channel restrictions:
The DS10, DS20, DS20E, ES40, GS80, GS160, and GS320
systems only support MC2 hardware.
If you configure a cluster with a single rail Memory Channel in
standard hub mode and the hub fails, every cluster member panics.
They panic because no member can see any of the other cluster
members over the Memory Channel interface.
A quorum disk does not
help in this case, because no system is given the opportunity to
obtain ownership of the quorum disk and survive.
To prevent this situation in standard hub mode, install a second
Memory Channel rail.
A hub failure on one rail will cause failover to the
other rail.
When the Memory Channel is set up in standard hub mode, the Memory Channel
hub must be visible to each member's Memory Channel adapter.
If the hub is
powered off, no system is able to boot.
A two-node cluster configured in virtual hub mode does not have
these problems.
In virtual hub mode, each system is always
connected to the virtual hub.
A loss of communication over the
Memory Channel causes both members (if both members are still up) to
attempt to obtain ownership of the quorum disk.
The member that
succeeds continues as a single-member cluster.
The other member
panics.
A single system of a two-node cluster that is configured in
virtual hub mode will boot because a virtual hub is always
present.
If a TruCluster Server cluster configuration utilizes multiple
Memory Channel adapters in standard hub mode, the Memory Channel adapters must
be connected to separate Memory Channel hubs.
The first Memory Channel adapter
(mca0) in each system must be connected to one
Memory Channel hub.
The second Memory Channel adapter (mcb0)
in each system must be connected to a second Memory Channel hub.
Also,
each Memory Channel adapter on one system must be connected to the same
linecard in each Memory Channel hub.
If redundant Memory Channel adapters are used with a DS10, they must be
jumpered for 128 MB and not the default of 512 MB.
If you have redundant MC2 modules on a GS80, GS160, or
GS320 system jumpered for 512 MB, you cannot have any other
modules except the CCMFB fiber-optic module on that PCI bus.
Redundant Memory Channels are supported within a mixed
Memory Channel configuration, as long as MC1 adapters are connected
to other MC1 adapters and MC2 adapters are connected to
MC2 adapters.
In a cluster with mixed revision Memory Channel rails, the MC2 adapter
modules must be jumpered for 128 MB.
A Memory Channel interconnect can use either virtual hub
mode (two member systems connected without a Memory Channel hub) or
standard hub mode (two or more systems connected to a hub).
A
TruCluster Server cluster with three or more member systems must be
jumpered for standard hub mode and requires a Memory Channel hub.
If Memory Channel modules are jumpered for virtual hub mode, all
Memory Channel modules on a system must be jumpered in the same manner,
either virtual hub 0 (VH0) or virtual hub 1 (VH1).
You cannot have
one Memory Channel module jumpered for VH0 and another jumpered for VH1 on
the same system.
The maximum length of an MC1 BC12N link
cable is 3 meters (9.8 feet).
The maximum length of an MC2 BN39B link
cable is 10 meters (32.8 feet).
In an MC2 configuration, you can use a CCMFB optical
converter in conjunction with the MC2 CCMAB host bus adapter or
a CCMLB hub line card to increase the distance between systems.
The BN34R fiber-optic cable, which is used to connect two CCMFB
optical converters, is available in 10-meter (32.8-foot) (BN34R-10)
and 31-meter (101.7-foot) (BN34R-31) lengths.
Customers may provide
their own fiber-optic cables to achieve greater separation of
systems.
The Memory Channel fiber-optic connection may be up to 2
kilometers (1.24 miles) between two CCMFB optical converters
connected to CCMAB host bus adapters in virtual hub mode.
The Memory Channel fiber-optic connection may be up to 3 kilometers
(1.86 miles) between a CCMFB optical converter connected to a CCMAB
host bus adapter and a CCMFB optical converter connected to a CCMLB
hub line card in standard hub mode (providing a maximum separation of
6 kilometers (3.73 miles) between systems).
Always examine a Memory Channel link cable for bent or broken pins.
Be sure that you do not bend or break any pins when you connect or disconnect
a cable.
For AlphaServer 8200, 8400, GS60, GS60E, or GS140 systems, the
Memory Channel adapter must be installed in slots 0-7 of a DWLPA PCIA
option; there are no restrictions for a DWLPB.
For AlphaServer 1000A systems, the Memory Channel adapter must
be installed on the primary PCI (in front of the PCI-to-PCI bridge chip) in
PCI slots 11, 12, or 13 (the top three slots).
For AlphaServer 2000 systems, the B2111-AA module must be
at Revision H or higher.
For AlphaServer 2100 systems, the B2110-AA module must be
at Revision L or higher.
Use the
examine
console command to determine if these
modules are at a supported revision as follows:
P00>>> examine -b econfig:20008
econfig: 20008 04
P00>>>
If a hexadecimal value of 04 or greater is returned, the I/O module
supports Memory Channel.
If a hexadecimal value of less than 04 is returned, the I/O module is
not supported for Memory Channel usage.
Order an H3095-AA module to upgrade an AlphaServer 2000 or an
H3096-AA module to upgrade an AlphaServer 2100 to support Memory Channel.
For AlphaServer 2100A systems, the Memory Channel adapter must be
installed in PCI 4 through PCI 7 (slots 6, 7, 8, and 9), which are the
bottom four PCI slots.
2.3 Host Bus Adapter Restrictions
To connect a member system to a shared SCSI bus, you must install a
host bus adapter in an I/O bus slot.
The Tru64 UNIX operating system supports a maximum of 64 I/O
buses.
&W4TCRfullname supports a total of 32 shared I/O buses using
KZPSA-BB host bus adapters, KZPBA-CB UltraSCSI
host bus adapters, or KGPSA Fibre Channel host bus adapters.
The following sections describe the host bus adapter restrictions in more detail.
2.3.1 Fibre Channel Requirements and Restrictions
Table 2-1
lists the supported AlphaServer
systems with Fibre Channel and the number of KGPSA-BC or KGPSA-CA
PCI-to-Fibre Channel adapters that are supported on each system at the
time the TruCluster Server Version 5.1A product was shipped.
For
the latest information about supported hardware, see the
AlphaServer options list for your system at the following URL:
http://www.compaq.com/alphaserver/products/options.html
Table 2-1: AlphaServer Systems Supported for Fibre Channel
The following requirements and restrictions apply to the use of Fibre
Channel with TruCluster Server Version 5.1A:
The HSG60 and HSG80 require Array Control Software (ACS)
Version 8.5 or later.
Eight member systems may be connected to common storage over
Fibre Channel in a fabric (switch) configuration.
A maximum of
two member systems is supported in arbitrated loop configurations.
The Fibre Channel RAID Array 8000 (RA8000) midrange
departmental storage subsystem and Fibre Channel Enterprise Storage
Array 12000 (ESA12000) house two HSG80 dual-channel controllers.
There are provisions for six UltraSCSI channels.
A maximum
of 72 disks is supported.
TheStorageWorks Modular Array 6000 (MA6000) supports
dual-redundant HSG60 controllers and 1-inch universal drives.
The StorageWorks Modular Array 8000 (MA8000) and Enterprise
Modular Array 12000 (EMA12000) support dual redundant HSG80
controllers and 1-inch universal drives.
The HSG60 or HSG80 Fibre Channel array controller support
only disk devices.
The only supported Fibre Channel adapters are the KGPSA-BC
and KGPSA-CA PCI-to-Fibre Channel host bus adapters.
The
KGPSA-BC adapter is supported in fabric configurations only; the
KGPSA-CA adapter is supported in either fabric or arbitrated loop
configurations.
The KGPSA-BC/CA PCI-to-Fibre Channel adapters are only supported on the
DWLPB PCIA option; they are not supported on the DWLPA.
The only supported Fibre Channel hub is the 7-port DS-SWXHB-07.
The DS-SWXHB-07 has clock and data recovery on each port.
It also
features Gigabit Interface Converter (GBIC) transceiver-based port
connections for maximum application flexibility.
The hub is hot
pluggable and is unmanaged.
Only single-hub arbitrated loop configurations are
supported; that is, there are no cascaded hubs on any SCSI
bus.
The only Fibre Channel switches supported are the
DS-DSGGA-AA/AB 8/16 port, DS-DSGGB-AA/AB 8/16 port, or
DS-DSGGC-AA/AB 8/16 port Fibre Channel switches.
The DSGGA, DSGGB, and DSGGC Fibre Channel switches and
the DS-SWXHB-07 hub support both shortwave (GBIC-SW) and
longwave (GBIC-LW) Gigabit Interface Converter (GBIC) modules.
Seven of the eight DSGGC-AA ports are fixed shortwave optical
transceivers.
Only one DSGGC-AA port is configured as a removable
GBIC.
It may be shortwave or longwave.
The GBIC-SW module supports 50-micron, multimode fiber cables
with the standard subscriber connector (SC) connector in lengths
up to 500 meters (1640.4 feet).
It also supports 62.5-micron multimode fiber
cables in lengths up to 200 meters (656.2 feet).
The GBIC-LW supports
9-micron, single-mode fiber cables with the SC connector in
lengths up to 10 kilometers (6.2 miles).
The KGPSA-BC/CA PCI-to-Fibre Channel host bus adapters and the
HSG60 and HSG80 RAID controller support the 50-micron Gigabit
Link Module (GLM) for fiber connections.
Therefore, only the
50-micron multimode fiber optical cable is supported between the
KGPSA and switch (or hub) and the switch (or hub) and HSG60 or
HSG80 for cluster configurations.
You must install GBIC-SW GBICs
in the Fibre Channel switches (or hub) for communication between
the switches (or hub) and KGPSA or HSG60/HSG80.
Tru64 UNIX Version 5.1A allows up to 255 Fibre Channel
targets.
An active host port or host bus adapter
constitutes a target.
Tru64 UNIX Version 5.1A allows up to 255 logical unit numbers (LUNs) per target.
The HSG60 and HSG80 supports transparent and multiple-bus failover mode
when used in a TruCluster Server Version 5.1A configuration.
Multiple-bus failover is recommended.
A storage array with dual-redundant HSG60 or HSG80 controllers in
transparent mode failover is two targets and consumes four ports on a
switch.
Transparent mode is recommended only while upgrading
from Tru64 UNIX Version 4.x.
After the
upgrade is complete, you should switch to multiple-bus failover.
A storage array with dual-redundant HSG60 or HSG80 controllers in
multiple-bus failover is four targets and consumes four ports on a switch.
The HSG60 and HSG80 documentation refers to the controllers
as Controllers A (top) and B (bottom).
Each controller provides
two ports (left and right).
(The HSG60 and HSG80 documentation
refers to these ports as Port 1 and 2, respectively.) In
transparent failover mode, only one left port and one right port
are active at any given time.
With transparent failover enabled, assuming that the left port of the
top controller and the right port of the bottom controller are active,
if the top controller fails in such a way that it can no longer
properly communicate with the switch, then its functions will
fail over to the bottom controller (and vice versa).
In transparent failover mode, you can configure which
controller presents each HSG60 or HSG80 storage element (unit) to
the cluster.
Ordinarily, the connections on port 1 (left port)
have a default unit offset of 0, and units designated D0 through
D99 are accessed through port 1 of either controller.
The
connections on port 2 (right port) have a default unit offset of
100, and units designated D100 through D199 are accessed through
port 2 of either controller.
In multiple-bus failover mode, the connections on all ports
have a default unit offset of 0, and all units (D0 through D199) are
visible to all host ports, but accessible only through one controller
at any specific time.
The host can control the failover process by
moving units from one controller to the other controller.
The Fibre Channel Tape Controller, Fibre Channel Tape
Controller II, TL891, TL895, and ESL9326D are supported on a
Fibre Channel storage bus.
For more information, see the
Enterprise Backup Solution with Legato NetWorker User Guide.
Legato NetWorker Version 6.0 is required for application
failover.
Tapes are single-stream devices.
There is no load
balancing of I/O requests over the available paths to the tape
devices.
The first available path to the tape devices is
selected for I/O.
2.3.2 KZPSA-BB SCSI Adapter Restrictions
KZPSA-BB SCSI adapters have the following restrictions:
The KZPSA-BB requires A12 firmware.
If you have a KZPSA-BB adapter installed in an
AlphaServer that supports the
bus_probe_algorithm
console variable (for example, the AlphaServer 800, 1000, 1000A, 2000,
2100, or 2100A systems), you must
set the
bus_probe_algorithm
console variable to
new
by entering the following command:
>>> set bus_probe_algorithm new
Use the
show bus_probe_algorithm
console command to
determine if your system supports the variable.
If the response is
null or an error, there is no support for the variable.
If the
response is anything other than
new, you must set
it to
new.
On AlphaServer 1000A and 2100A systems, updating the firmware on
the KZPSA-BB SCSI adapter is not supported when the adapter is behind the
PCI-to-PCI bridge.
2.3.3 KZPBA-CB SCSI Bus Adapter Restrictions
KZPBA-CB UltraSCSI adapters have the following restrictions:
A maximum of four HSZ50, HSZ70, or HSZ80 RAID array controllers can be placed
on a single KZPBA-CB UltraSCSI bus.
Only two redundant pairs of array
controllers are allowed on one SCSI bus.
The KZPBA-CB requires ISP 1020/1040 firmware Version 5.57 or higher,
which is available with the system SRM console firmware on the Alpha
Systems Firmware 5.3 Update CD-ROM (or later).
The maximum length of any differential SCSI bus segment is
25 meters (82 feet), including the length of the SCSI bus cables
and SCSI bus internal to the SCSI adapter, hub, or storage
device.
A SCSI bus may have more than one SCSI bus segment (see
Section 3.1).
See the KZPBA-CB UltraSCSI Storage Adapter Module
Release Notes
for more information.
2.4 Disk Device Restrictions
The restrictions for disk devices are as follows:
2.5 RAID Array Controller Restrictions
RAID array controllers provide high performance, high availability, and high
connectivity access to SCSI devices through a shared SCSI bus.
RAID array controllers require the minimum Array Controller
Software (ACS) listed in
Table 2-2.
Table 2-2: RAID Controller Minimum Required Array Controller Software
| RAID Controller |
Minimum Required
Array Controller Software |
| HSZ20 |
3.4 |
| HSZ22 (RAID Array 3000) |
D11x |
| HSZ40 |
3.7 |
| HSZ50 |
5.7 |
| HSZ70 |
7.7 |
| HSZ80 |
8.3-1 |
| HSG60 |
8.5 |
| HSG80 |
8.5 |
RAID controllers can be configured with the number of SCSI IDs as
listed in
Table 2-3.
Table 2-3: RAID Controller SCSI IDs
| RAID Controller |
Number of SCSI IDs
Supported |
| HSZ20 |
4 |
| HSZ22 (RAID Array 3000) |
2 |
| HSZ40 |
4 |
| HSZ50 |
4 |
| HSZ70 |
8 |
| HSZ80 |
15 |
| HSG60 |
N/A |
| HSG80 |
N/A |
The following restrictions are imposed for support of the StorageWorks
RAID Array 3000 (RA3000) subsystem:
The RAID Array 3000 (RA3000) with HSZ22 controller does not
support multi-bus access or multiple-bus failover.
You cannot
achieve a no-single-point-of-failure (NSPOF) cluster using an
RA3000.
The KZPBA-CB UltraSCSI host adapter is the only SCSI bus host
adapter supported with the RA3000 in a TruCluster Server cluster.
The KZPBA-CB requires ISP 1020/1040 firmware Version 5.57 (or higher),
which is available with the system SRM console firmware on the Alpha Systems
Firmware 5.4 or later Update CD.
Only RA3000 storage units visible to the host as LUN0
(storage units with a zero (0) as the last digit of the unit
number such as D0, D100, D200, and so forth) can be used as a
boot device.
StorageWorks Command Console (SWCC) V2.2 is the only
configuration utility that will work with the RA3000.
SWCC V2.2
runs only on a Microsoft Windows NT or Windows 2000 PC.
The controller will not operate without at least one 16-MB
SIMM installed in its cache.
The device expansion shelf (DS-SWXRA-GN) for the rackmount
version must be at revision level B01 or higher.
The single-ended personality module used in the
DS-SWXRA-GN UltraSCSI storage expansion shelves must be at
revision H01 or higher.
The RA3000 order includes an uninterruptible power supply (UPS),
which must be connected to the RA3000.
2.6 SCSI Signal Converters
If you are using a standalone storage shelf with a single-ended
SCSI interface in your cluster configuration, you must connect it to a
SCSI signal converter.
SCSI signal converters convert wide,
differential SCSI to narrow or wide, single-ended SCSI and vice versa.
Some signal converters are standalone desktop units and some are
StorageWorks building blocks (SBBs) that you install in storage
shelves disk slots.
Note
UltraSCSI hubs logically belong in
this section because they contain a DOC (DWZZA on a chip) chip,
but they are discussed separately in
Section 2.7.
The restrictions for SCSI signal converters are as follows:
If you remove the cover from a standalone unit, be sure to
replace the star washers on all four screws that hold the cover in place when
you reattach the cover.
If the washers are not replaced, the SCSI signal
converter may not function correctly because of noise.
If you want to disconnect a SCSI signal converter from a shared
SCSI bus, you must turn off the signal converter before disconnecting the
cables.
To reconnect the signal converter to the shared bus, connect the
cables before turning on the signal converter.
Use the power switch to turn
off a standalone SCSI signal converter.
To turn off an SBB SCSI signal
converter, pull it from its disk slot.
If you observe any "bus hung" messages, your DWZZA
signal converters may have the incorrect hardware.
In addition, some DWZZA
signal converters that appear to have the correct hardware revision may cause
problems if they also have serial numbers in the range from
CX444xxxxx through CX449xxxxx.
To upgrade a DWZZA-AA or DWZZA-VA signal converter to the
correct revision, use the appropriate field change order (FCO), as follows:
DWZZA-AA-F002
DWZZA-VA-F001
2.7 DS-DWZZH-03 and DS-DWZZH-05 UltraSCSI Hubs
The DS-DWZZH-03 and DS-DWZZH-05 series UltraSCSI hubs are the
only hubs that are supported in a TruCluster Server configuration.
They are SCSI-2- and draft SCSI-3-compliant SCSI 16-bit signal
converters capable of data transfer rates of up to 40 MB/sec.
These hubs can be listed with the other SCSI bus signal
converters, but because they are used differently in cluster
configurations, they are discussed differently in this manual.
A DS-DWZZH-03 or DS-DWZZH-05 UltraSCSI hub can be installed in:
A StorageWorks UltraSCSI BA356 shelf (which has the required
180-watt power supply).
The lower righthand device slot of the BA370 shelf within the
RA7000 or ESA 10000 RAID array subsystems.
This position minimizes cable
lengths and interference with disks.
A wide BA356 that has been upgraded to the 180-watt power
supply with the DS-BA35X-HH option.
A DS-DWZZH-03 or DS-DWZZH-05 UltraSCSI hub:
Improves the reliability of the detection of cable faults.
Provides for bus isolation of cluster systems while allowing
the remaining connections to continue to operate.
Allows for more separation of systems and
storage in a cluster configuration, because each SCSI bus segment
can be up to 25 meters (82 feet) in length.
This allows a total
separation of nearly 50 meters (164 feet) between a system and
the storage.
Note
The DS-DWZZH-03/05 UltraSCSI hubs cannot be connected to a
StorageWorks BA35X storage shelf because the storage shelf does not
provide termination power to the hub.
2.8 SCSI Cables
If you are using shared SCSI buses, you must determine if you
need cables with connectors that are low-density 50-pins,
high-density 50-pins, high-density 68-pins (HD68), or VHDCI
(UltraSCSI).
If you are using an UltraSCSI hub, you will need
HD68-to-VHDCI and VHDCI-to-VHDCI cables.
In some cases, you also
have the choice of straight or right-angle connectors.
In
addition, each supported cable comes in various lengths.
Use the
shortest possible cables to adhere to the limits on SCSI bus
length.
Table 2-4
describes each supported cable
and the context in which you would use the cable.
Some Compaq
equivalent 6-3 part numbers are not provided.
Table 2-4: Supported SCSI Cables
| Cable |
Connector Density |
Pins |
Configuration Use |
| BN21W-0B |
Three high |
68-pin |
A Y cable that can be attached to a
KZPSA-BB or KZPBA-CB if there is no room for a trilink connector.
It can be used with a terminator to provide external termination. |
| BN21M |
One low, one high |
50-pin LD to 68-pin HD |
Connects the single-ended end of a
DWZZA-AA or DWZZB-AA to a TZ885 or TZ887.
[Footnote 6]
|
| BN21K, BN21L, or 328215-00X |
Two HD68 |
68-pin |
Connects BN21W Y cables or wide devices.
For example, connects KZPBA-CBs, KZPSA-BBs, HSZ40s, HSZ50s, the differential sides
of two SCSI signal converters, or a DWZZB-AA to a BA356. |
| BN37A |
Two VHDCI |
VHDCI to VHDCI |
Connects two VHDCI trilinks to each
other or an UltraSCSI hub to a trilink on an HSZ70, HSZ80, or an
UltraSCSI hub to a RAID Array 3000. |
| BN38C or BN38D |
One HD68, one VHDCI |
HD68 to VHDCI |
Connects a KZPBA-CB or KZPSA-BB to a
port on an UltraSCSI hub.
|
| BN38E-0B |
Technology adapter cable |
HD68 male to VHDCI female |
May be connected to a BN37A cable
and the combination used in place of a BN38C or BN38D cable |
| 199629-002 or 189636-002 |
Two high |
50-pin HD to 68-pin HD |
Connect a Compaq 20/40 GB DLT Tape
Drive to a DWZZB-AA |
| 146745-003 or 146776-003 |
Two high |
50-pin HD to 50-pin HD |
Daisy-chain two Compaq 20/40 GB DLT
Tape Drives |
| 189646-001 or 189646-002 |
Two high |
68-pin HD |
Connect a Compaq 40/80 DLT Tape
Drive to a DWZZB-AA or daisy-chain two Compaq 40/80 DLT Tape Drives |
Always examine a SCSI cable for bent or broken pins.
Be sure
that you do not bend or break any pins when you connect or disconnect a cable.
2.9 SCSI Terminators and Trilink Connectors
Table 2-5
describes the supported trilink connectors and SCSI terminators and the context
in which you use them.
Table 2-5: Supported SCSI Terminators and Trilink Connectors
| Trilink Connector or Terminator |
Density |
Pins |
Configuration
Use |
| H885-AA |
Three |
68-pin |
Trilink
connector that attaches to high-density, 68-pin cables or devices,
such as a KZPSA-BB, KZPBA-CB, HSZ40, HSZ50, or the differential side
of a SCSI signal converter.
Can be terminated with an H879-AA
terminator to provide external termination. |
| H8574-A or H8860-AA |
Low |
50-pin |
Terminates a TZ885 or TZ887 tape drive. |
| 341102-001 |
High |
50-pin |
Terminates a Compaq 20/40 GB DLT
Tape Drive |
| H879-AA or 330563-001 |
High |
68-pin |
Terminates an H885-AA trilink connector,
BN21W-0B Y cable, or an ESL9326D Enterprise Library tape drive. |
| H8861-AA |
VHDCI |
68-pin |
VHDCI trilink connector that
attaches to VHDCI 68-pin cables, UltraSCSI BA356 JA1, and HSZ70 or HSZ80
RAID controllers.
Can be terminated with an H8863-AA terminator if
necessary. |
| H8863-AA |
VHDCI |
68-pin |
Terminate a VHDCI trilink connector. |
| 152732-001 |
VHDCI |
68-pin |
Low Voltage Differential terminator |
The requirements for trilink connectors are as follows:
If you connect a SCSI cable to a trilink connector, do not
block access to the screws that mount the trilink, or you will be unable to
disconnect the trilink from the device without disconnecting the cable.
Do not install an H885-AA trilink if installing it
will block an adjacent peripheral component interconnect (PCI) port.
Use a BN21W-0B Y cable instead.